Considering the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) certification? You’re in good company. As organizations increasingly lean on digital technology, the demand for professionals skilled in securing and auditing information systems is growing. The CISA certification, governed by ISACA, has become the global benchmark for those working in IT auditing, control, and security. With the rising importance of cybersecurity and risk management, obtaining this certification not only enhances your credibility but also positions you favorably in a competitive job market.

Key Takeaways
- High Demand: CISA-certified professionals are increasingly sought after, reflecting the urgent need for skilled auditors in the evolving digital landscape.
- Global Recognition: The CISA certification is recognized worldwide as the standard for IT auditing, validating your expertise and opening doors to global opportunities.
- Comprehensive Exam: Understanding the exam structure, including its challenging format and scoring system, is crucial for effective preparation and success.
- Variety of Resources: Multiple study resources, ranging from official materials to online courses, cater to different learning styles and preferences, ensuring that you can find the right fit for your study plan.
But how do you navigate this challenging exam and ensure success? This guide dives deep into the ISACA CISA certification process, the best study resources, and detailed exam preparation strategies to help you succeed. Whether you’re just starting your journey or looking to refine your study plan, this comprehensive guide is here to support you every step of the way.
A Brief History of the ISACA CISA Certification
The CISA certification was introduced by ISACA to address the growing need for skilled information systems auditors in the late 1970s. Initially, it focused on auditing and control within financial institutions but has since evolved to cover a broader spectrum of information systems and cybersecurity topics. Over the decades, the certification has been updated to reflect the latest standards and practices, ensuring that CISA-certified professionals are well-prepared to tackle modern cybersecurity challenges.
Why get an ISACA CISA Certification?

The world of information security auditing is evolving at an unprecedented pace. As technology continues to integrate into every facet of business, the demand for information security auditors has surged year after year. With ongoing changes in IT, cybersecurity threats, and regulatory landscapes, the need for CISA-certified professionals has never been greater. Major financial institutions and banks worldwide are actively recruiting CISA-certified candidates to perform effective security assessments, leading to increased job opportunities and improved salaries across the board.
As cyber threats escalate and regulatory requirements become more stringent, organizations are prioritizing the protection of their IT infrastructures. Here are several compelling reasons to pursue the CISA certification:
1. Enhanced Credibility
The CISA credential is globally recognized and highly respected across various industries. Holding this certification validates your expertise in Information Systems (IS) auditing, control, and assurance. It signals to employers that you possess the necessary knowledge and skills to assess and manage risks effectively, thereby enhancing your professional credibility.
2. Career Advancement
Achieving CISA certification can significantly accelerate your career trajectory. It opens doors to senior positions such as:
- IT Audit Manager: Oversee audit teams and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Risk Manager: Identify and mitigate potential risks to an organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Compliance Officer: Ensure that the organization adheres to industry standards and regulations.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Lead the organization’s cybersecurity strategy and initiatives.
With the CISA credential, you position yourself as a strong candidate for leadership roles in information security.
3. Increased Earning Potential
According to ISACA’s salary surveys, CISA-certified professionals can earn 20-30% more than their non-certified peers. Salaries for CISA holders typically range between $90,000 and $140,000 annually, depending on experience, location, and industry. This increase in earning potential is a compelling incentive for many professionals to pursue CISA certification.
4. High Industry Demand
The rise of cyber-attacks and data breaches has led to a significant demand for skilled information systems auditors and security experts across multiple sectors, including finance, healthcare, and technology. Organizations are increasingly seeking CISA-certified professionals to ensure their IT environments are secure and compliant with industry regulations. This trend highlights the importance of CISA certification as a pathway to a stable and rewarding career.
5. Versatile Skill Set
The CISA certification equips you with a comprehensive skill set that is applicable across various domains, including:
- Risk Management: Understand and implement effective risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
- Compliance and Governance: Ensure that organizational policies align with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- IT Service Management: Learn how to manage and improve IT service delivery in alignment with business objectives.
These versatile skills make you a valuable asset to any organization, enhancing your employability and career resilience in an ever-changing job market.
6. Networking Opportunities
Being CISA-certified connects you to a global network of professionals in the field of information security. Through ISACA, you gain access to exclusive events, webinars, and forums where you can share knowledge, learn from industry leaders, and stay updated on the latest trends in IT governance and security. Networking with fellow professionals can lead to new job opportunities, mentorship, and collaborative projects.
7. Commitment to Continuous Learning
Pursuing the CISA certification demonstrates your commitment to professional development and lifelong learning. The certification requires ongoing education and renewal, ensuring that you stay current with evolving technologies, regulations, and best practices in information security. This commitment not only enhances your skill set but also reflects positively on your dedication to your profession.
Understanding the ISACA CISA Certification Process
1. Eligibility Requirements
To qualify for the CISA exam, candidates must meet specific criteria established by ISACA. These requirements ensure that applicants have a foundational level of experience and knowledge in the field of information systems auditing, control, or security. Here’s a breakdown of the eligibility requirements:
Professional Experience
- Minimum Requirement: You need at least five years of professional work experience in relevant areas, including information systems auditing, control, or security.
- Waiver Options: If you don’t have the full five years, you can waive up to three years of this requirement through specific qualifications:
- 1-Year Waiver: Holding a bachelor’s or master’s degree in a related field (e.g., computer science, information technology, or accounting) can waive one year of experience.
- 1-Year Waiver: Possessing a related professional certification, such as CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) or CISM (Certified Information Security Manager), also qualifies for a one-year waiver.
- 2-Year Waiver: Completing a full-time university program related to information systems can waive up to two years of experience, even if the program was completed over ten years ago.
Documentation
- Application Process: When applying for the exam, candidates must submit an application that includes detailed descriptions of their professional experience. It is critical to document your experience accurately, as ISACA may require verification or additional information. Having clear, quantifiable examples of your work can help substantiate your claims.
2. How to Apply for the CISA Exam: Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the CISA exam application process is straightforward if you follow these steps:
Step 1: Create an ISACA Profile
Begin by creating an account on the ISACA website. This account will serve as your central hub for all activities related to your certification.
Step 2: Submit the Exam Application
Complete the CISA exam application form. Be prepared to provide comprehensive details about your professional experience, including your job roles, responsibilities, and the duration of each position held. This transparency is crucial for a successful application.
Step 3: Pay the Exam Fee
The exam fee varies depending on your ISACA membership status:
- For Members: The fee is approximately $575.
- For Non-Members: The fee is around $760.
- Consider becoming a member of ISACA, as the membership can significantly reduce your costs and provide additional resources.
Step 4: Schedule the Exam
After your application is approved, you will receive instructions on how to schedule your exam. You can choose to take the exam at a Pearson VUE testing center or opt for online remote proctoring, which allows for greater flexibility.
Step 5: Prepare for the Exam
Preparation is key to success in the CISA exam. Utilize a combination of self-study resources, such as textbooks and online courses, and formal training programs offered by recognized providers. Engaging with practice exams can also help familiarize you with the exam format and types of questions.
3. ISACA CISA Certification Maintenance and CPE Requirements
Once you earn your CISA certification, maintaining it is essential for continued professional development and compliance with ISACA standards. Here are the requirements for certification maintenance:
Continuing Professional Education (CPE) Requirements
- To maintain your certification, you must complete 20 CPE hours each year and accumulate 120 CPE hours over a three-year period. CPE activities can include:
- Attending industry conferences and workshops
- Participating in webinars and online training sessions
- Engaging in self-study or academic courses
- Contributing to professional publications or serving as a speaker at events
- CPE opportunities not only help you stay current with industry developments but also enhance your skills and knowledge, making you a more valuable asset to your organization.
Annual Maintenance Fee
- In addition to completing CPE requirements, certified professionals are required to pay an annual maintenance fee to keep their certification active. This fee supports ISACA’s ongoing efforts to provide valuable resources and maintain the integrity of the certification program.
ISACA CISA Certification Exam Breakdown: Domains and Weights
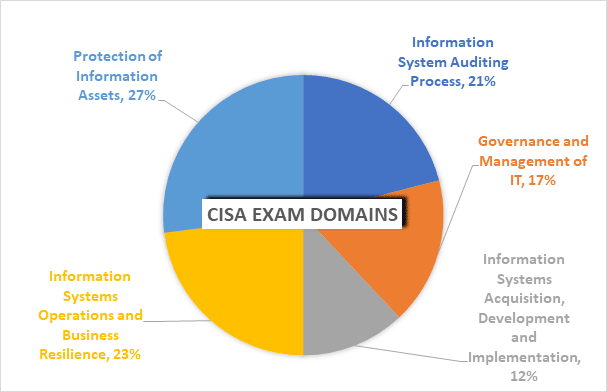
The CISA exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions spread across five domains, each representing a vital area of expertise for Information Systems (IS) auditors. Understanding the weight and focus of each domain is crucial for effective study planning. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of each domain, its key topics, and the percentage of questions allocated to it.
| Domain | Weight | Key Topics |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Information Systems Auditing Process | 21% | – Audit Planning – Evidence Collection Techniques – Sampling Methodologies – Reporting and Communication |
| 2. Governance and Management of IT | 17% | – IT Governance Frameworks – IT Strategy Alignment – Performance Measurement – Risk Management |
| 3. Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation | 12% | – Project Management Practices – Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) – Business Case Development – Post-implementation Reviews |
| 4. Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience | 23% | – IT Operations Management – Incident Management – Business Continuity Planning (BCP) – Data Backup and Recovery |
| 5. Protection of Information Assets | 27% | – Security Policies and Standards – Access Controls and Authentication – Cryptography and Data Protection – Security Awareness Training |
Detailed Domain Breakdown
1. Information Systems Auditing Process (21%)
This domain emphasizes the essential principles and practices that govern information systems auditing. Mastery of this domain is vital for preparing comprehensive audit plans and executing effective audits.
- Audit Planning: Involves developing a roadmap for audits, including scope, objectives, and resources.
- Evidence Collection Techniques: Focuses on various methods to gather evidence, ensuring that audits are grounded in factual data.
- Sampling Methodologies: Learn how to select samples that accurately reflect the entire population, increasing the reliability of audit results.
- Reporting and Communication: Understand how to present findings clearly and concisely, ensuring stakeholders understand the implications of the audit.
2. Governance and Management of IT (17%)
This domain explores the frameworks and strategies necessary to align IT initiatives with overarching business goals. Effective governance is crucial for ensuring that IT investments deliver value.
- IT Governance Frameworks: Discusses models like COBIT and ITIL that help organizations manage their IT resources effectively.
- IT Strategy Alignment: Examines methods to ensure that IT strategies support business objectives, enhancing overall performance.
- Performance Measurement: Covers metrics and KPIs that assess the effectiveness and efficiency of IT governance.
- Risk Management: Focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with IT operations.
3. Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation (12%)
This domain focuses on the processes involved in acquiring and implementing information systems that align with business needs. Understanding this domain is essential for effective project management.
- Project Management Practices: Discusses methodologies like Agile and Waterfall that guide successful project delivery.
- Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC): Covers phases from requirement gathering to system deployment and maintenance.
- Business Case Development: Focuses on creating compelling business cases for IT projects, outlining expected benefits and costs.
- Post-implementation Reviews: Examines how to evaluate system performance after implementation, ensuring objectives are met.
4. Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience (23%)
This domain addresses the operational aspects of managing information systems, focusing on maintaining continuity and minimizing disruptions.
- IT Operations Management: Involves overseeing day-to-day IT activities to ensure optimal performance and service delivery.
- Incident Management: Discusses processes for identifying, managing, and resolving IT incidents promptly.
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP): Focuses on preparing for unforeseen events that could disrupt operations, ensuring that critical functions can continue.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Covers strategies for protecting data and ensuring its availability in case of loss or corruption.
5. Protection of Information Assets (27%)
As the largest domain, this area emphasizes safeguarding information systems against various threats. Professionals must be well-versed in security practices to protect sensitive data.
- Security Policies and Standards: Discusses the importance of establishing clear security guidelines that govern IT practices.
- Access Controls and Authentication: Covers methods to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Cryptography and Data Protection: Explains techniques for securing data, including encryption and tokenization.
- Security Awareness Training: Highlights the need for ongoing education to ensure all employees understand security protocols and practices.
ISACA CISA Certification Exam Scoring and Evaluation
The ISACA CISA Certification exam is scored on a scale of 200 to 800, with a passing score of 450. This score reflects the minimum level of knowledge necessary to effectively perform as a CISA-certified professional. The exam aims to assess both theoretical knowledge and practical application in real-world scenarios.
| Scoring Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Scaled Scoring | Each question is weighted differently based on difficulty, contributing more to your overall score if challenging. |
| Passing Criteria | A minimum score of 450 is required to pass, indicating competency in the subject matter. |
| Score Reporting | Preliminary results are available immediately after the exam, while official scores are released approximately two weeks later. |
By understanding the breakdown of the CISA exam domains and their respective weights, candidates can tailor their study plans effectively, ensuring they allocate appropriate time and resources to each area. This structured approach not only enhances knowledge retention but also boosts confidence on exam day.
Detailed Study Strategies for Each CISA Domain
These are the most important tips to keep in mind when preparing for each of the CISA exam domains.
1. Information Systems Auditing Process
Study Tip:
Focus on understanding core audit principles, methodologies, and the overall auditing lifecycle. Familiarize yourself with the steps involved in conducting an audit, from planning and risk assessment to fieldwork and reporting. Practice creating detailed audit plans that identify objectives, scope, resources, and timelines. Learn to perform risk assessments by identifying potential risks and determining their impact and likelihood.
Resources:
- Case Studies: Analyze real-world scenarios to see how audit principles are applied in various industries. Consider how organizations identify risks, set objectives, and measure controls.
- Books and Journals: Look for resources like “IT Auditing: Using Controls to Protect Information Assets” by Chris Davis, which provides practical insights into auditing.
- ISACA Resources: Utilize ISACA’s guidelines on audit methodologies, which often include frameworks and templates to aid your study.
2. Governance and Management of IT
Study Tip:
Familiarize yourself with various IT governance frameworks such as COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) and ISO/IEC 38500. Understand how to align IT strategy with overall business objectives by grasping the principles of strategic alignment, value delivery, resource management, and performance measurement. Engage in exercises that require you to map IT initiatives to organizational goals.
Resources:
- ISACA Guides: For in-depth coverage of governance frameworks and their practical application, refer to ISACA’s IT Governance and Risk Management guides.
- Webinars and Workshops: Participate in ISACA webinars and local chapter workshops to engage with professionals who can share their insights on governance challenges and best practices.
- Industry Reports: Explore reports from consulting firms like Gartner and Deloitte that discuss IT governance trends and case studies of successful implementations.
3. Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation
Study Tip:
Concentrate on project management methodologies, particularly the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC), and understand each phase’s role in ensuring successful IT project delivery. Study the responsibilities of IS auditors in overseeing IT projects, including assessing project controls and ensuring compliance with standards. Familiarize yourself with Agile, Waterfall, and DevOps methodologies to understand different approaches to project management.
Resources:
- Project Management Books: For fundamental concepts and techniques, consider reading “A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide).”
- Online Courses: To gain practical insights, enroll in courses related to project management and SDLC on platforms like Coursera or LinkedIn Learning.
- ISACA Publications: Use ISACA’s resources on project management and system development to understand how auditors assess and ensure the quality of IT projects.
4. Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience
Study Tip:
Emphasize the importance of IT operations management, business continuity planning (BCP), and disaster recovery planning (DRP). Study real-world case studies that highlight significant business disruptions, such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks, and analyze how organizations respond. Focus on best practices in incident response, crisis management, and recovery strategies to ensure business resilience.
Resources:
- ISACA Materials: Utilize ISACA’s BCP and DRP guides, which outline frameworks for creating and implementing effective business continuity strategies.
- Simulation Exercises: Engage in tabletop exercises or simulations that allow you to practice developing BCP and DRP strategies in a controlled environment.
- Industry Publications: Read white papers and case studies published by organizations like the Business Continuity Institute (BCI) that illustrate successful business continuity practices.
5. Protection of Information Assets
Study Tip:
Master the principles of data protection, access controls, and comprehensive information security management. Understand the various types of security controls (preventive, detective, and corrective) and how they are applied in safeguarding information assets. Review case studies of notable security breaches to learn how they occurred, the response measures taken, and lessons learned to mitigate similar incidents.
Resources:
- ISACA Security Management Guides: For thorough coverage of information security concepts and frameworks, refer to ISACA’s security management and data protection resources.
- Security Certifications: To deepen your understanding of information security practices, consider studying for other relevant certifications, such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
- Online Forums: Join online forums and discussion groups (like those on ISACA Engage) to engage with other professionals and gain insights on emerging threats and mitigation strategies.

Building Hands-On Experience for ISACA CISA Certification
While theoretical knowledge is crucial for passing the CISA exam, hands-on experience can set you apart from other candidates in the competitive job market. Gaining practical experience not only reinforces your learning but also enhances your problem-solving skills and boosts your confidence. Here are some effective strategies to accumulate relevant hands-on experience:
1. Participate in IT Audits
Engaging in IT audits is one of the most direct ways to gain hands-on experience related to the CISA domains. If you’re already working in an IT or risk management role, consider volunteering to assist with internal or external audits. Here’s how to get involved:
- Seek Opportunities Within Your Organization: Approach your supervisor or audit team and express your interest in participating in upcoming audits. Offer to help with document reviews, data analysis, or on-site assessments.
- Join Professional Groups: Consider joining local chapters of ISACA or other professional organizations that conduct audits. Networking with professionals in these groups can open doors to audit-related projects.
- Learn Audit Tools: Familiarize yourself with common auditing software and tools like ACL, IDEA, or TeamMate. Proficiency in these tools can enhance your contributions and make you a more valuable team member.
2. Work on IT Governance Projects
Involvement in IT governance initiatives can significantly deepen your understanding of the frameworks that guide IT management and risk assessment. Here’s how you can engage:
- Volunteer for Governance Committees: If your organization has committees focused on IT governance, offer to participate. This involvement can provide insight into decision-making processes and compliance requirements.
- Implement Frameworks: Take the initiative to help implement governance frameworks such as COBIT, ITIL, or ISO 27001. Understand how these frameworks influence policy development, risk management, and compliance.
- Document Policies and Procedures: Work on documenting existing policies or developing new ones. This experience will hone your ability to translate governance principles into actionable procedures and enhance your understanding of regulatory requirements.
3. Develop Business Continuity Plans
Contributing to your organization’s business continuity and disaster recovery planning is invaluable, particularly for mastering Domain 4 of the CISA exam, which focuses on business continuity. Here’s how to get involved:
- Participate in Risk Assessments: Assist in conducting risk assessments to identify critical business functions and potential disruptions. This experience will enhance your analytical skills and your understanding of risk management.
- Draft and Review Plans: Offer to draft or review business continuity plans. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the components of effective plans, such as recovery strategies and communication protocols.
- Conduct Drills and Training: Help organize and participate in business continuity drills. Understanding how to execute plans in real scenarios will provide practical insights into their effectiveness and areas for improvement.
4. Engage in Continuous Learning and Networking
Beyond specific projects, ongoing education and networking are crucial for building hands-on experience:
- Attend Workshops and Seminars: Participate in workshops or webinars focused on IT audit, governance, and risk management. These events often include case studies or group activities that provide practical experience.
- Seek Mentorship: Connect with a mentor who is experienced in the CISA domains. A mentor can provide guidance, share experiences, and help you navigate challenges in your learning journey.
- Join Professional Associations: Becoming an active member of professional organizations like ISACA can provide access to resources, study groups, and networking opportunities with experienced professionals.
By actively seeking out these hands-on experiences, you can not only prepare yourself for the CISA exam but also enhance your employability and readiness for a successful career in IT auditing and governance.
Exploring the CISA Job Market and Career Opportunities
Earning your CISA certification can significantly enhance your career prospects. Here’s a snapshot of the job market and potential roles:
Common Job Roles for CISA Professionals
- IT Auditor: Conducts audits of IT systems and processes to ensure compliance with policies and regulations.
- Information Security Manager: Oversees the organization’s information security strategy, including the protection of sensitive data.
- Risk Manager: Identifies and mitigates risks related to IT systems, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Compliance Officer: Ensures the organization adheres to legal and regulatory requirements related to IT and data security.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Responsible for the organization’s overall information security strategy and implementation.
Salary Insights
- Entry-Level: $70,000 – $90,000
- Mid-Level: $90,000 – $120,000
- Senior-Level: $120,000 – $160,000+
Industries Hiring CISA Professionals
- Financial Services: Organizations prioritize IT security and compliance due to stringent regulatory requirements.
- Healthcare: Increasingly focused on protecting patient data and complying with regulations like HIPAA.
- Government and Defense: Strong emphasis on safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining national security.
- Technology and Consulting: Rapid growth in IT consulting firms seeking CISA professionals to enhance their service offerings.
Future Outlook
The demand for CISA-certified professionals is expected to grow as organizations prioritize IT security and compliance. Emerging fields like cloud security, data privacy, and cybersecurity will continue to create new opportunities for CISA holders. By gaining hands-on experience and obtaining your CISA certification, you position yourself as a valuable asset in this evolving job market.
Essential Steps to Successfully Prepare for the ISACA CISA Certification
1. Become An Accountant
While the CISA certification focuses on information systems auditing, a solid grounding in accounting principles is vital. Understanding accounting fundamentals will help you grasp how IT systems support financial reporting and internal controls. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Understanding Financial Statements: Familiarize yourself with balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. This knowledge is crucial for assessing the impact of IT systems on financial data integrity.
- Internal Controls: Learn about the different types of internal controls and how they relate to IT processes. This will help you understand the audit process better and identify risks related to financial reporting.
- Regulatory Compliance: Gain insight into regulations such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), which mandate specific internal control standards for financial reporting. Understanding these regulations will help you navigate the compliance aspects of IT auditing effectively.
Enhancing your accounting skills will provide a strong foundation for your CISA exam preparation and your future career in IT auditing.
2. Read The Most Important CISA Study Materials
The CISA Review Manual (CRM) from ISACA is essential for your exam preparation. Here’s why you’ll find it both challenging and invaluable:
- Comprehensive Coverage: The CRM is designed to cover all the topics included in the CISA exam. It provides a detailed explanation of key concepts, frameworks, and practices that you must understand.
- Roles and Responsibilities: The manual not only outlines the skills needed for the CISA exam but also clarifies the roles and responsibilities of IS auditors, helping you grasp what’s expected in real-world scenarios.
- Multiple Readings: It’s recommended to read the CRM multiple times to reinforce your understanding. Each read will deepen your comprehension and reveal new insights that may have been missed initially.
To supplement your study, consider other recommended resources such as the CISA Exam Guide and relevant academic journals to broaden your knowledge base.
3. CISA Study Planner
Effective planning is essential for CISA exam success, especially for those juggling full-time jobs. Here’s how to create an effective study plan:
- Time Management: Allocate at least 1-2 hours each evening to focus on your studies. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks to avoid burnout.
- Recommended Study Breakdown:
- 35% on the CRM: Dive deep into the manual, making notes and summarizing key points.
- 20% on Coaching: Join study groups or engage with peers who are also preparing for the CISA exam. Discussion can clarify difficult concepts and provide new perspectives.
- 45% on Simulations/Practice Tests: Regularly take practice exams to gauge your knowledge and identify areas that need improvement. Simulations can mimic the real exam environment, which helps with time management.
Creating a structured study plan will ensure you cover all necessary material and increase your chances of passing the exam on your first attempt.
4. Use The Free CISA Study Materials
ISACA offers several free resources that can kickstart your CISA preparation. Utilize these valuable tools to supplement your studies:
- ISACA Candidate Start Guide: This guide provides an overview of the exam process, including registration, exam dates, and key policies.
- CISA Self-Assessment Quiz: This quiz can help you identify your strengths and weaknesses before diving deep into your studies, allowing you to tailor your preparation accordingly.
- Information Security Audit Guide: Familiarize yourself with common practices in information security audits. This guide will provide insights into audit methodologies and frameworks relevant to the exam.
Leveraging these free materials will give you a head start without incurring additional costs.
5. Practical Information Security Audit Experience
Gaining hands-on experience in information security audits is crucial for your CISA journey. Here’s how to effectively prepare:
- Networking Opportunities: Attend industry conferences, workshops, and local ISACA chapter meetings. These events provide valuable networking opportunities and insights from experienced professionals.
- Engage with IT Security Processes: Seek opportunities within your current job or through internships to get involved in IT security processes. This experience will help you understand the practical application of your studies.
- Connect with CISA Professionals: Reach out to CISA-certified individuals on platforms like LinkedIn. Engaging with them can provide insights into best practices, challenges, and tips for successfully navigating the CISA exam.
Practical experience will not only enrich your knowledge but also make you a more competitive candidate in the job market.
6. CISA Courses
Investing in a quality CISA prep course can significantly enhance your chances of success. Here’s what to consider when selecting a course:
- Types of Courses: Options range from online self-paced courses to live instructor-led sessions. Choose the format that fits your learning style and schedule best.
- Course Content: Ensure the course includes practice exams, video lectures, multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and instructor support. These components will help you grasp complex topics and prepare effectively.
- Cost vs. Value: While some courses may be more expensive, consider the potential value they provide in terms of comprehensive material and support. A solid prep course can often make a difference in your exam performance.
By following these guidelines and utilizing a combination of resources and strategies, you’ll position yourself for success in your CISA certification journey. With dedication, thorough preparation, and practical experience, passing the CISA exam on your first try is within reach.
FAQs About ISACA CISA Certification
What are the prerequisites for obtaining the ISACA CISA certification?
To qualify for the CISA certification, you need a minimum of five years of professional experience in information systems auditing, control, or security. However, some educational and professional certifications can substitute for a portion of this experience.
How long does it take to prepare for the CISA exam?
The preparation time can vary widely depending on your background and study habits. On average, candidates spend 3 to 6 months studying for the CISA exam. A structured study plan can help you make the most of your time.
What is the format of the CISA exam?
The CISA exam consists of 150 multiple-choice questions covering five domains of knowledge. It is offered in a computer-based format at authorized testing centers and takes four hours to complete.
What is the passing score for the CISA exam?
To pass the CISA exam, candidates must achieve a scaled score of 450 or higher out of a possible 800. The scoring system is based on the difficulty of the questions you answered correctly.
How often do I need to renew my ISACA CISA certification?
CISA certification holders must renew their certification every three years by earning Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits. To maintain the certification, a total of 20 CPE hours must be earned annually.
Bottom Line: Your Path to CISA Success
Earning your CISA certification is a significant milestone that can dramatically enhance your career trajectory in IT auditing, information security, and risk management. This certification not only validates your expertise but also demonstrates your commitment to the field, making you a highly sought-after candidate in today’s job market. With the increasing reliance on technology and the rising threats to information security, organizations are actively seeking professionals who can navigate complex security landscapes.
To maximize your chances of success, consider the following steps:
- Create a Structured Study Plan: Allocate specific times each week dedicated to your study sessions. Break down the material by domain, allowing yourself to absorb the information fully before moving on to the next topic.
- Utilize a Variety of Resources: Explore different learning formats, including textbooks, video lectures, and interactive quizzes. This multifaceted approach will cater to various learning styles and help reinforce your understanding of complex topics.
- Engage with Study Groups: Connect with other CISA candidates or professionals in the field. Study groups can provide valuable insights, motivation, and support, as well as opportunities for discussing challenging concepts.
- Gain Hands-On Experience: Seek out internships, volunteer opportunities, or projects within your current job that allow you to apply audit principles in real-world settings. This practical experience will reinforce your learning and build your confidence.
- Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Information security is an ever-evolving field. Regularly reading industry publications, attending webinars, and participating in networking events will help you stay current on best practices and emerging threats.
With determination and the right strategy, you’ll be well on your way to achieving your CISA certification and unlocking a wealth of career opportunities. For more information on CISA certification and to explore various prep courses, visit the ISACA website or consult with your organization’s training department.