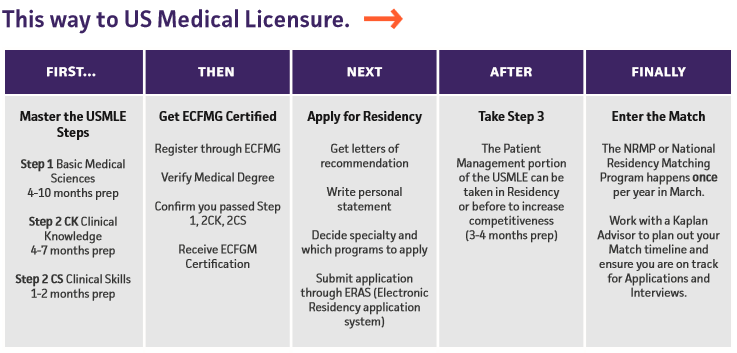
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) is one of the most significant milestones in a medical student’s journey to becoming a licensed physician in the United States. This rigorous examination ensures doctors possess the necessary knowledge, clinical skills, and decision-making abilities to provide safe and effective patient care. Whether you aim to practice medicine in the U.S. or prepare for residency, the USMLE exam is a key component of your medical career.
If you’re a medical student or graduate planning to practice medicine in the U.S., you must pass all parts of the USMLE exam. The exam is divided into three main steps that assess everything from foundational medical knowledge to the ability to apply that knowledge in real-world clinical settings. It’s not just about knowing facts—it’s about proving you can think critically and make decisions that affect patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- The USMLE is a three-part exam required to become a licensed physician in the U.S.
- It tests your medical knowledge, clinical skills, and ability to apply them in real-life situations.
- Each step of the USMLE focuses on different aspects of medical practice—from basic science to independent patient care.
- Students need extensive preparation and knowledge in medical sciences, clinical decision-making, and patient management to pass the exam.
Throughout this article, we’ll break down what each step of the exam involves, what you can expect during the test, and provide tips on preparing for this essential medical examination. Understanding the structure and content of the USMLE is the first step toward passing with confidence.
Let’s dive into each step of the exam and the requirements, including how to prepare for the USMLE, what’s covered, and tips on achieving success!
What Is the USMLE Exam?

The USMLE is a national examination recognized across the United States and by various medical licensing boards. It’s jointly sponsored by the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME), both of which are responsible for creating, administering, and ensuring the integrity of the exam. These organizations collaborate to ensure that the USMLE accurately reflects current medical standards and prepares medical professionals for the evolving demands of the healthcare industry.
The exam assesses various medical knowledge, clinical skills, and problem-solving abilities across several steps. The USMLE ensures that anyone who passes can provide patients with safe, evidence-based, and effective care. The exam is divided into three distinct steps:
- USMLE Step 1: Focuses on foundational science knowledge.
- USMLE Step 2 CK (Clinical Knowledge): Tests your ability to apply medical knowledge in a clinical setting.
- USMLE Step 2 CS (Clinical Skills): Was once part of the exam but has since been discontinued.
- USMLE Step 3: Assesses your ability to provide independent care.
Each step evaluates a different aspect of medical practice, ensuring that you’re well-versed in theory and capable of applying your knowledge to real-world medical situations. Let’s dive deeper into the specific components of each step.
USMLE Step 1: The Foundations of Medicine
USMLE Step 1 begins your journey to becoming a licensed physician. This exam is designed to assess your understanding of the core scientific principles that form the foundation of modern medicine. It covers a broad range of subjects essential for practicing medicine, and your performance here plays a critical role in determining your readiness for more advanced clinical training in the later stages of your medical education.
Key Topics Covered in Step 1
Step 1 focuses on the basic sciences that underlie the medical practice. Some of the main subjects include:
- Anatomy: Understanding the structure of the human body and its systems.
- Physiology: Learning how the body’s systems function in health and disease.
- Biochemistry: Studying the chemical processes that occur within the body.
- Microbiology: Exploring pathogens, infections, and how the body defends itself.
- Pathology: Understanding disease mechanisms and the impact of diseases on the body.
- Pharmacology: Learning about drugs and their effects on the human body.
- Epidemiology and Public Health: Examining how diseases spread, are controlled, and affect populations.
The knowledge gained from these topics is crucial for understanding the human body in health and disease and making clinical decisions later in your career.
Exam Format and Structure
Step 1 is entirely multiple-choice, and you must answer up to 280 questions daily. The questions test your ability to recall key facts and apply your understanding of medical sciences to real-world clinical scenarios. The goal is to see how well you can use basic science principles in practice. While the exam is challenging, it is structured to ensure that those who pass are well-equipped to move on to more advanced stages of medical training.
Each question is crafted to evaluate your ability to think critically, make accurate judgments, and apply foundational knowledge to new situations—vital skills in every area of medical practice.
The Importance of Step 1 in Your Medical Journey
While Step 1 is focused on basic science knowledge, its importance cannot be overstated. The exam is a gateway to more advanced clinical training in the later stages of your career. A strong performance on Step 1 can help open doors to competitive residency programs, as residency programs often consider your Step 1 score when evaluating your application.
However, it’s important to note that while Step 1 tests your foundational knowledge, it’s not just about memorization. You’ll need to show that you can integrate your knowledge, apply it to different clinical contexts, and think critically about the information presented to you.
How to Prepare for Step 1
Preparing for Step 1 requires a well-structured study plan, as the exam covers a wide range of material. Here are a few tips to help guide your preparation:
- Start early: Give yourself plenty of time to absorb the material. Many students recommend starting to review core subjects well before the exam date.
- Use high-quality study resources: Resources like First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 and UWorld are widely used by students preparing for Step 1. They provide comprehensive overviews and practice questions that mirror the actual exam format.
- Practice actively: Simply reading through textbooks isn’t enough. Use practice questions to test your knowledge and improve your exam technique.
- Take breaks and stay healthy: Preparing for Step 1 can be intense, so don’t forget to take breaks and maintain a healthy lifestyle. A well-rested mind is key to performing your best on exam day.
By understanding the content covered and using the right preparation strategies, you’ll be well on your way to passing Step 1 and continuing your medical career.
USMLE Step 2 CK: Clinical Knowledge in Practice
USMLE Step 2 CK (Clinical Knowledge) is the next critical step in your journey toward becoming a physician. Unlike Step 1, which focuses on foundational sciences, Step 2 CK assesses your ability to apply this knowledge in real-world clinical settings. This exam emphasizes patient care, diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases, providing a thorough understanding of how medical knowledge translates into practical skills you’ll need during clinical practice.
Key Topics Covered in Step 2 CK
Step 2 CK covers a wide range of essential topics for patient care. The exam is designed to assess how well you can apply your medical knowledge to clinical scenarios, including:
- Cardiovascular Health: Diagnosing and treating heart-related conditions, including arrhythmias, heart failure, and myocardial infarctions.
- Musculoskeletal Health: Understanding and managing orthopedic conditions, fractures, arthritis, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Reproductive Health: Addressing women’s health, obstetrics, gynecology, and male reproductive issues.
- Respiratory Health: Diagnosing and treating respiratory diseases, such as asthma, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Infectious Diseases: Applying knowledge of microbiology and pharmacology to treat infections and prevent disease spread.
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: Assessing strategies for preventive care, immunization, and lifestyle changes to improve patient health.
- Patient Safety and Ethics: Questions related to patient safety, ethical issues in healthcare, professionalism, and legal matters that impact patient care.
The goal of Step 2 CK is to ensure that you are prepared to handle real-world clinical situations, interact effectively with patients, and contribute to developing treatment plans.
Exam Format and Structure
Step 2 CK, like Step 1, is multiple-choice but contains up to 318 questions spanning a broader range of topics. These questions test your ability to apply clinical knowledge, interpret patient data, and make informed decisions. The questions typically present a clinical vignette followed by possible diagnoses or treatment options, testing for critical thinking, and medical judgment.
The exam is divided into several blocks of questions, and you’ll have a specific amount of time to complete each section. This format mirrors clinical decision-making’s high-stakes, time-sensitive nature, helping assess your readiness to handle actual patient cases.
The Importance of Step 2 CK in Your Medical Career
Step 2 CK is vital in preparing you for clinical rotations and supervised patient care during residency. A strong performance in this exam demonstrates that you possess the clinical knowledge needed to provide effective patient care. Your Step 2 CK score is often considered by residency programs when evaluating applicants, and it reflects your clinical aptitude and ability to handle patient care responsibilities.
In addition to preparing you for residency, Step 2 CK also builds on the foundation laid by Step 1. It requires you to integrate the knowledge of basic medical sciences you gained in Step 1 and apply it in real-life patient scenarios. This integration is essential for providing holistic care and developing treatment plans for complex cases.
How to Prepare for Step 2 CK
Preparing for Step 2 CK requires a strategic approach, as the exam covers a broad spectrum of clinical topics. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Start early: Begin your review well in advance of the exam. Many students recommend starting dedicated Step 2 CK preparation several months before the test date.
- Use high-yield resources: Resources like UWorld, First Aid for the USMLE Step 2 CK, and OnlineMedEd are popular among students preparing for Step 2 CK. These provide comprehensive question banks, detailed explanations, and clinical insights that mimic the exam format.
- Focus on clinical vignettes: Since Step 2 CK is vignette-based, practice answering clinical scenario questions. Understanding how to approach and solve these cases will improve your performance.
- Simulate test conditions: Take practice exams under timed conditions to get a feel for the pacing of the real test. This will help you manage your time effectively on exam day.
- Review patient safety and ethics: Don’t overlook topics like patient safety, legal issues, and medical ethics, as these are integral to the exam and your future practice as a physician.
By following these preparation strategies and focusing on the clinical application of your knowledge, you’ll be well-prepared to succeed in Step 2 CK and take the next step toward your medical career.
USMLE Step 3: Independent Practice
USMLE Step 3 is the final exam in the USMLE series, and it plays a critical role in assessing your ability to provide independent, unsupervised care as a practising physician. Unlike earlier steps, which primarily focus on medical knowledge and basic science, Step 3 evaluates your clinical decision-making skills and readiness to manage patients autonomously in a clinical setting.
Structure and Content of Step 3
Step 3 is divided into two parts, typically taken over two separate days:
- Day 1: Foundations of Clinical Medicine
On the first day, the focus is on assessing your ability to perform basic clinical tasks. This includes:- Gathering Information: You must demonstrate how effectively you can take a patient’s history and obtain relevant information.
- Physical Examination: You’ll be evaluated on your ability to perform thorough physical exams and interpret findings.
- Initial Diagnostic Decision-Making: You’ll be tasked with making accurate initial diagnoses based on the information you gather from the patient.
- Day 2: Advanced Patient Management
The second-day shifts to more complex aspects of patient care, including:- Medical Decision-Making involves making informed decisions about treatment plans, interventions, and follow-up care.
- Health Maintenance and Screening: You will be tested on your understanding of preventive medicine, including health maintenance strategies and screening protocols for various diseases.
Exam Format and Structure
Step 3 includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and computer-based case simulations (CCS). The multiple-choice portion tests your knowledge of clinical concepts and ability to make decisions in various medical situations. The computer-based case simulations are designed to evaluate your clinical reasoning and ability to manage patient care in real-time, where you will be presented with virtual patient cases and must make decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care.
This format aims to replicate real-world clinical decision-making, testing how you apply your medical knowledge in various patient care scenarios.
The Importance of Step 3 in Your Medical Career
Step 3 is the final hurdle before obtaining your medical license, and it plays a key role in determining your readiness to practice independently. Step 3 signals to residency programs, hospitals, and licensing authorities that you possess the clinical judgment and skills to provide safe, effective patient care without supervision.
The skills you demonstrate in Step 3 will directly translate into your ability to make sound clinical decisions. A strong performance on Step 3 will help with licensure and serve as a valuable benchmark for your responsibilities as a practicing physician.
How to Prepare for Step 3
Effective preparation for Step 3 requires focusing on clinical knowledge and practical decision-making. Here are a few tips to guide your preparation:
- Review Clinical Guidelines and Protocols: Step 3 emphasizes real-world medical practices, so reviewing clinical guidelines and evidence-based protocols is essential for success. Refer to resources like the UpToDate or National Guideline Clearinghouse for current standards of care.
- Practice with Computer-Based Simulations: Case simulations can be challenging, so it’s important to practice managing virtual patient cases. Platforms like UWorld offer practice cases that closely mirror the format of Step 3.
- Focus on Time Management: Step 3 is time-intensive, especially during the computer-based simulations. Practice making quick, informed decisions under time pressure to simulate the real exam environment.
- Understand Preventive Medicine: Review health maintenance guidelines, screening protocols, and preventive care, as these are major areas on Day 2 of the exam.
By preparing with a focus on practical clinical scenarios and decision-making, you will be better equipped to handle the complexities of Step 3 and demonstrate your readiness to practice medicine independently.
Who Can Take the USMLE?

The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) is a crucial step for anyone aspiring to practice medicine in the U.S. It’s designed for medical students and graduates from both U.S. and international medical schools. However, your USMLE eligibility varies depending on your background and the medical school you attend. Here’s a breakdown to help you understand who can take each part of the exam:
1. Eligibility for Step 1 and Step 2
To sit for Step 1 and Step 2 of the USMLE, you must meet specific eligibility criteria:
- For U.S. and Canadian medical students: You are generally eligible to take these steps if you’re currently enrolled in an accredited MD (Doctor of Medicine) or DO (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) program. You’ll need to be in the appropriate stage of your medical education, typically after completing your first two years of coursework for Step 1 and before clinical rotations for Step 2 CK (Clinical Knowledge).
- For international students: If you attend a foreign medical school, you can also take the USMLE Steps. Still, you must meet the certification requirements set by the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). The ECFMG verifies that your medical school and education meet the standards set by U.S. medical licensing boards. You’ll need to apply for ECFMG certification before you can sit for Step 1 or Step 2.
Learn more about ECFMG certification here.
2. Eligibility for Step 3
Step 3 is a bit different from Steps 1 and 2. To sit for Step 3, which assesses your ability to provide independent care, you must meet the following requirements:
- Complete Steps 1 and 2: You need to have passed both Step 1 and Step 2 CK before you can sit for Step 3.
- Graduation from an accredited medical school: In addition to completing the first two steps, you must have graduated from an accredited medical school. This includes U.S., Canadian, and international institutions recognized by the appropriate licensing authorities.
If you’re a graduate of a U.S. or Canadian medical school, you’ll be automatically eligible for Step 3 once you’ve passed Steps 1 and 2.
However, for international medical graduates, in addition to meeting the above requirements, you’ll need to provide proof of your ECFMG certification to be eligible to take Step 3.
Check out more about Step 3 eligibility on the official USMLE website.
3. Other Considerations
- Timeframe: Most candidates take Steps 1 and 2 while still in medical school, and Step 3 is generally taken after graduation, during or after clinical training.
- Residency program requirements: In many cases, residency programs require you to pass Step 1 and Step 2 CK before applying. Some programs may also require Step 3, particularly if you’re applying for advanced residency positions.
In summary, whether you’re attending a U.S., Canadian, or international medical school, you must meet specific requirements to take each step of the USMLE. The key for international students is obtaining ECFMG certification to ensure eligibility.
If you’re uncertain about your eligibility or the application process, visit the official USMLE eligibility page and the ECFMG website for further details. Is a good idea
How Long Is the USMLE Exam?
The USMLE exams are known for their demanding nature in terms of content and the time required to complete them. The exam process spans multiple days and can be mentally exhausting, but proper preparation can make a significant difference in managing the time and staying focused.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the time commitment for each step of the USMLE exam:
Step 1: Duration and Structure
- Total Time: Up to 8 hours of testing.
- Structure: The exam is divided into seven 60-minute blocks, each containing a maximum of 40 questions. This structure requires knowledge and the ability to maintain concentration for extended periods.
- Breaks: You’ll have short breaks between blocks, with one optional break lasting 45 minutes after completing the first four blocks.
Step 1 focuses on basic science subjects like anatomy, biochemistry, microbiology, and pharmacology. It’s often considered the most intense because it requires both speed and accuracy in answering the multiple-choice questions.
Step 2 CK (Clinical Knowledge): Duration and Structure
- Total Time: Up to 9 hours.
- Structure: The exam consists of eight 60-minute blocks, each containing up to 40 questions.
- Breaks: Like Step 1, you’ll have scheduled breaks between blocks and an optional 45-minute break in the middle.
Step 2 CK tests your ability to apply medical knowledge in clinical settings. You will answer questions about diagnosing and managing various medical conditions across specialties, from internal medicine to pediatrics.
Step 3: Duration and Structure (Two Days)
- Day 1:
- Total Time: Up to 7 hours.
- Structure: This day includes six 60-minute blocks, totaling up to 240 questions.
- Day 2:
- Total Time: Up to 9 hours.
- Structure: On the second day, there are six 45-minute blocks, with a maximum of 270 questions.
- Breaks: On both days, you will have a 45-minute break between certain blocks, allowing you to recharge.
Step 3 is divided into two days, with Day 1 focused on foundational clinical knowledge and Day 2 emphasizing patient management and decision-making in a more independent context. The goal of Step 3 is to assess your readiness to practice medicine unsupervised.
Total Time for All Three Steps
If you plan to take all three steps of the USMLE exam, the total time required to complete all sections is approximately 33 hours. This is spread across multiple days, with Step 3 being the longest due to its two-day format.
It’s important to note that while the USMLE exams are intense, you’ll have access to official USMLE resources and practice exams that can help you familiarize yourself with the time structure and the types of questions you’ll face.
Tips for Managing Time During the Exam
The time constraints during the USMLE exams are part of the challenge, but effective preparation can help you stay on track. Here are some tips:
- Practice Timed Tests: Take practice exams under timed conditions to understand the time needed for each question.
- Pace Yourself: Aim to finish each block early so you have time to review your answers, especially for the more difficult questions.
- Take Advantage of Breaks: Use your breaks to hydrate and recharge. A short walk or a quick snack can help refresh your mind.
- Stay Calm: The exam length can be intimidating, but staying calm and focused is key to maintaining daily performance.
You can find more helpful exam tips and resources on the USMLE website. By understanding the structure and planning, you’ll be better prepared to handle the exam’s long hours, making it easier to focus on demonstrating your knowledge and clinical skills.
How Much Is the USMLE Exam?
The cost of taking the USMLE exam varies based on your location and the specific step of the exam you’re taking. Medical students and graduates face different application procedures and associated fees, whether in the U.S., Canada, or internationally. Let’s break down the costs so you know exactly what to expect.
USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK Costs
For medical students and graduates based in the U.S. and Canada, the fees for Step 1 and Step 2 CK (Clinical Knowledge) are administered by the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME). Here’s what you need to know about their costs:
- Step 1: $645
- Step 2 CK: $645
The process is slightly different if you are a medical student or graduate from international schools (outside of the U.S. and Canada). You will apply through the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG), and the fees for each step are as follows:
- Step 1: $985
- Step 2 CK: $985
The application fees for both Step 1 and Step 2 CK are higher for international students, reflecting the additional administrative work involved in processing international applications.
USMLE Step 3 Costs
For all medical school graduates, regardless of whether they’re from the U.S., Canada, or abroad, USMLE Step 3 is administered by the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB). The application fee for Step 3 is $895. This step is typically taken after medical school and often during or after a residency program.
Total USMLE Exam Cost
Here’s how the total costs break down for each group of applicants:
- For U.S. and Canadian medical students:
The combined cost for Steps 1, 2 CK, and Step 3 is $2185. - For international medical students:
The combined cost for Steps 1, 2 CK, and Step 3 is $2865.
These costs cover the application fees for all the steps. Still, they don’t include additional expenses such as study materials, prep courses, or travel for testing (for international students, this may involve additional logistics and costs).
Important Points to Consider:
- Re-taking the USMLE:
If you don’t pass any of the steps on your first try, you must pay the application fee again to retake the exam. This could add significant costs depending on how many attempts are necessary. - Payment Options:
Most students pay for the exams through their respective institutions, or they may pay directly when registering on the NBME, ECFMG, or FSMB websites. Reviewing the payment methods and deadlines well in advance is important to avoid any last-minute issues.
Is the USMLE Exam Worth the Cost?
With its hefty price tag, it’s natural to wonder whether the USMLE is worth the investment. The USMLE is a critical step toward becoming a licensed physician, and it serves as a standardized way to assess medical knowledge and clinical competency. Passing the exam is essential for anyone wishing to practice medicine in the U.S. and can significantly improve career prospects.
However, it’s also important to be mindful of the expenses involved. Aside from the exam fees, students and graduates often invest in study resources, prep courses, and practice tests to ensure success. These resources can also add to the cost of preparing for the exam. For a comprehensive look at prep materials, check out our guide on USMLE preparation resources for more insights.
How Hard Is the USMLE Exam?
The USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination) is regarded as one of the most challenging exams aspiring doctors will face. It’s about testing how much you know and assessing how well you can apply that knowledge in real-life clinical situations. The difficulty of the exam lies in its broad scope, which includes everything from basic medical sciences to complex patient care scenarios.
A Broad Range of Topics
The USMLE tests knowledge across multiple disciplines, including:
- Basic Medical Sciences include anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, and microbiology. It forms the foundation for understanding how the human body works and how diseases affect it.
- Clinical Skills – The exam evaluates how well you can apply your knowledge to diagnose and treat patients. This includes understanding how to gather patient histories, perform physical exams, and make clinical decisions.
- Medical Ethics and Professionalism – You’ll also be tested on your ability to handle complex ethical dilemmas and interact with patients professionally. This ensures that future physicians practice integrity and respect patients’ rights.
Given the broad scope of topics covered in the exam, it’s no surprise that preparation can be intense and time-consuming.
The Complexity of Application
One of the reasons the USMLE is so challenging is that it doesn’t just focus on rote memorization. Instead, it asks you to apply your knowledge in clinical scenarios. For instance, rather than just asking you to recall the symptoms of a disease, the exam might present you with a virtual patient and ask you to choose the most appropriate course of action, considering their medical history, symptoms, and other relevant factors. This is especially true in later steps, like Step 2 (Clinical Knowledge) and Step 3, which focus heavily on patient care and decision-making.
Time and Effort Needed for Preparation
Because of the exam’s vast material and application-based nature, preparing for the USMLE requires significant time and effort. The amount of study time needed varies by individual, but on average, students spend months preparing for each step of the exam. The preparation process includes:
- Studying core subjects: You must master fundamental subjects like pathology, pharmacology, and microbiology. Focus on high-yield content, information most commonly tested on the exam.
- Practice Questions and Simulations: Familiarizing yourself with the exam format is crucial for success. Many resources offer practice questions and test simulations that help you understand how the real exam will look and feel.
- UWorld is among the most popular resources for practice questions and step-by-step explanations.
- The NBME offers official practice exams for a fee to help gauge your readiness.
- Prep Courses: Many students enroll in USMLE prep courses (like Kaplan or AMBOSS) to get a structured study plan and expert guidance. These courses often include online resources, textbooks, and video lectures that cover the essential topics in-depth.
Managing the Mental Challenge
Beyond the extensive material, the exam also demands mental endurance. The length and intensity of the exam days can take a toll on even the most prepared candidates. For example, Step 1 can take up to 8 hours, and Step 2 CK can take up to 9 hours of testing, making stamina an important factor in success. In addition to technical preparation, stress management, and mental preparation are essential.
What Makes the USMLE So Challenging?
- Comprehensive Content: The exam doesn’t focus on just one specialty but covers a wide range of medical knowledge.
- Clinical Application: It’s not just about what you know—it’s about how you apply that knowledge to real-life scenarios.
- Time Pressure: The exam is long, and the pressure of the clock can increase stress, making concentration challenging.
- Complex Cases: Step 2 and Step 3 present you with complex patient cases that require a deep understanding of the medical decision-making process.
Preparing for Success
Although the USMLE is difficult, it’s not impossible. You can be well-prepared for the challenge with the right strategy and resources. Here are a few tips to help you succeed:
- Create a Study Schedule: Start early and stick to a study plan. This helps to break down the overwhelming amount of material into manageable portions.
- Use Trusted Resources: Stick to reputable and high-yield materials. Popular resources like First Aid for the USMLE and Pathoma are frequently recommended by those who’ve passed the exam.
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Take full-length practice exams under timed conditions to get used to the pacing and format.
- Join a Study Group: Discussing difficult topics with peers can help reinforce concepts and offer new perspectives.
The USMLE is undeniably challenging, but you can conquer it with the right preparation and resources. Use trusted prep materials, simulate the real exam experience, and maintain a steady study pace to give yourself the best shot at success. Remember, you’re not just memorizing facts; you’re training to become a doctor who can provide excellent patient care.
For more guidance, you can explore USMLE prep courses and practice exams. You’re not alone on this journey, and the resources available can help you every step of the way.
What Is a Good Score on the USMLE Exam?
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) is a critical assessment for medical professionals aiming to practice in the United States. Each of its three steps evaluates different competencies, and understanding the scoring system is essential for aspiring physicians.
USMLE Step 1: Transition to Pass/Fail
In January 2022, the USMLE Step 1 transitioned to a pass/fail scoring system. To pass, candidates must achieve a score of 196. This change was implemented to reduce stress and allow residency programs to focus on other aspects of an applicant’s profile.
USMLE Step 2 CK and Step 3: Three-Digit Scoring
Unlike Step 1, Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) and Step 3 use a three-digit scoring system. The minimum passing scores are:
- Step 2 CK: 209
- Step 3: 200 (effective January 1, 2024)
Aiming Beyond the Minimum
While meeting the minimum passing scores is essential, striving for higher scores can enhance your competitiveness for residency programs and demonstrate a stronger grasp of medical knowledge. For instance, a Step 2 CK score of 220 is often considered more competitive.
Summary Table: USMLE Passing Scores
| USMLE Step | Passing Score |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Pass/Fail (196) |
| Step 2 CK | 209 |
| Step 3 | 200 (effective January 1, 2024) |
Note: The passing score for Step 1 is reported as pass/fail, with a minimum score of 196.
Understanding these scoring systems and aiming for scores above the minimum can significantly impact your medical career trajectory.
Final Thoughts
The USMLE is an essential milestone in becoming a licensed physician in the United States. While the process may seem daunting due to the comprehensive nature of the exam, it is designed to ensure that physicians have the foundational knowledge, clinical skills, and decision-making abilities necessary to provide high-quality care to patients. Each exam step is carefully structured to assess a physician’s capabilities, from understanding basic medical sciences to applying that knowledge in real-world clinical settings and making independent medical decisions.
Success in the USMLE requires strategic preparation, persistence, and using resources such as practice exams, review courses, and study materials. Remember that high scores make you more competitive when applying for residency programs, so aiming for excellence can open doors to more prestigious opportunities.
The exam is not just a hurdle to clear but an important part of your development as a physician. It ensures you’re well-prepared for the complexities of patient care and meets the rigorous standards expected in the medical profession. By dedicating sufficient time to each step of the process, seeking help when needed, and staying committed, you’ll set yourself up for success in your medical career.
While the USMLE exam is challenging, it’s also an opportunity to demonstrate your competence and readiness to practice medicine. Approach it with a clear study plan, the right resources, and a confident mindset, and you will be well on your way to becoming a licensed physician.
